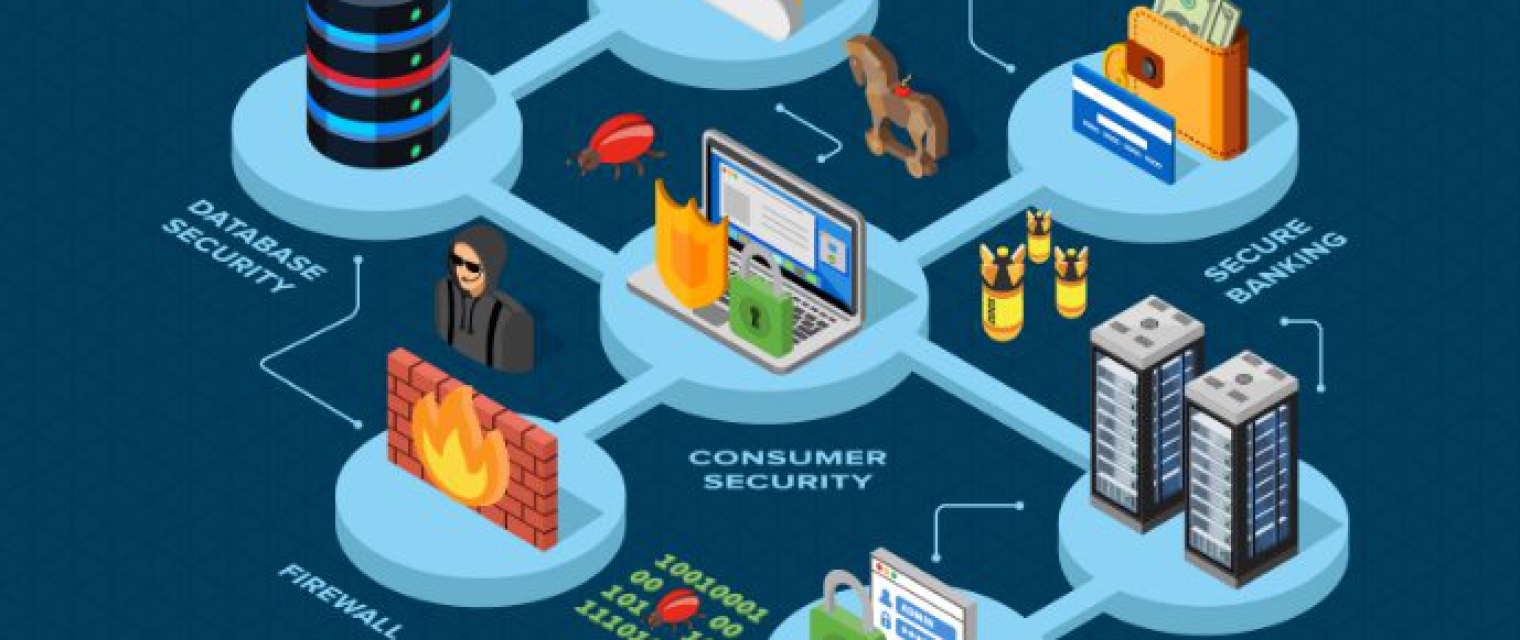
Data Encryption
Secure Encryption Of Your Company Data
Data is a critical part of every business, but this most valuable asset often poses a huge risk when it travels or is transmitted beyond your
...
DDoS Protection
DDoS attacks can come out of the blue and escalate quickly. A successful attack can have a huge impact, disrupting business continuity and damaging both customer and brand
...
Web Security
The Internet has become an indispensable business tool, yet browsing the Web has never been more dangerous.
Attackers now utilise the Web as the primary means for delivering viruses and
...
SIEM & Log Management
Security information and event management (SIEM) technology supports threat detection and security incident response through the real-time collection and historical analysis of security events
...
Next Generation Firewalls
A firewall is the main line of defence for your IT network, keeping your network safe from cyber intrusion.
A firewall can help prevent hackers or malicious software from gaining access
...
Endpoint Protection
Protection of files in your network must be a top priority for your business. Our endpoint protection solutions will protect your server and individual workstations from malware and viruses that
...